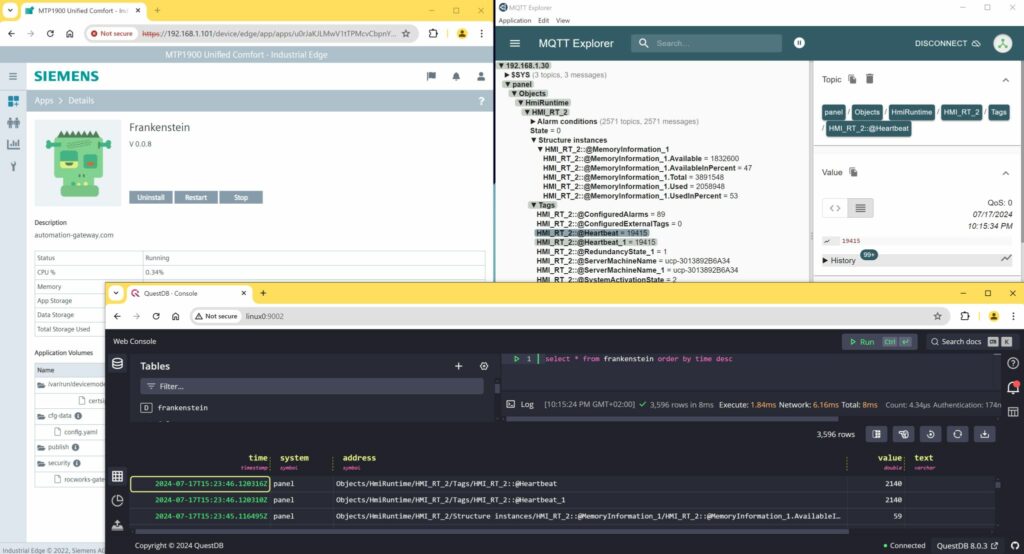
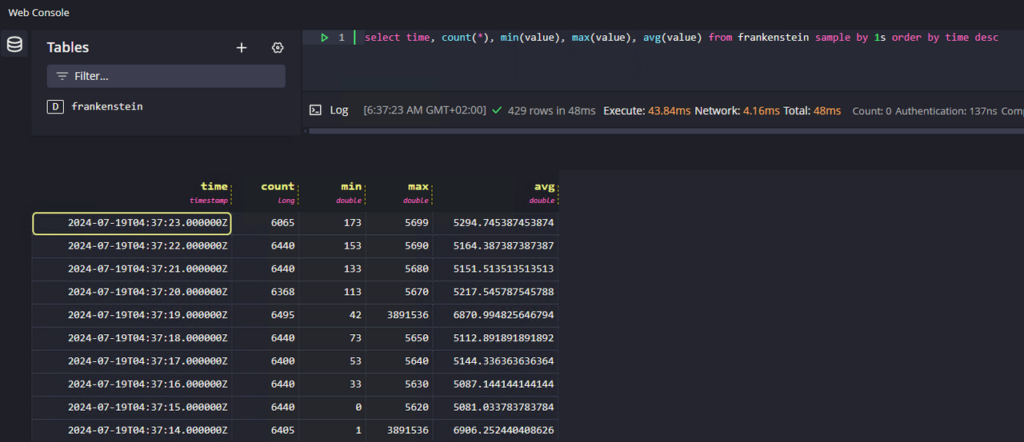
Initially you have to init the certbot and get the certificate manually.
# Directories used:
/var/www
/var/www/certbot # handshake sites from certbot
/etc/letsencrypt # certificates are stored here
# Initialize Certbot:
docker run --rm -ti \
-v /var/www:/var/www \
-v /etc/letsencrypt:/etc/letsencrypt \
certbot/certbot certonly --webroot -w /var/www/certbot -d <yor-domain-name> --email your.email@something.com
The letsencrypt and the www directory must be mounted on both containers. Certbot will check the certificates every 12h and nginx must reload the configuration periodically.
nginx:
image: nginx:1.17.8
ports:
- 80:80
- 443:443
volumes:
- /var/www:/var/www
- /etc/nginx.conf:/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
- /etc/letsencrypt:/etc/letsencrypt
command: "/bin/sh -c 'while :; do sleep 6h & wait $${!}; nginx -s reload; done & nginx -g \"daemon off;\"'"
certbot:
image: certbot/certbot
restart: unless-stopped
volumes:
- /var/www:/var/www
- /etc/letsencrypt:/etc/letsencrypt
entrypoint: "/bin/sh -c 'trap exit TERM; while :; do certbot renew --webroot -w /var/www/certbot; sleep 12h & wait $${1}; done;'"
Nginx must be configured to publish the certbots well-known sites for the handshake and your sites must be configured to use the certificates from letsencrypt.
server {
listen 80;
server_name <your-domain-name>;
server_tokens off;
location /.well-known/acme-challenge/ {
root /var/www/certbot;
}
location / {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
}
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name vcm.winccoa.at;
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/<your-domain-name>/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/<your-domain-name>/privkey.pem;
root /var/www;
index index.html;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ =404;
}